
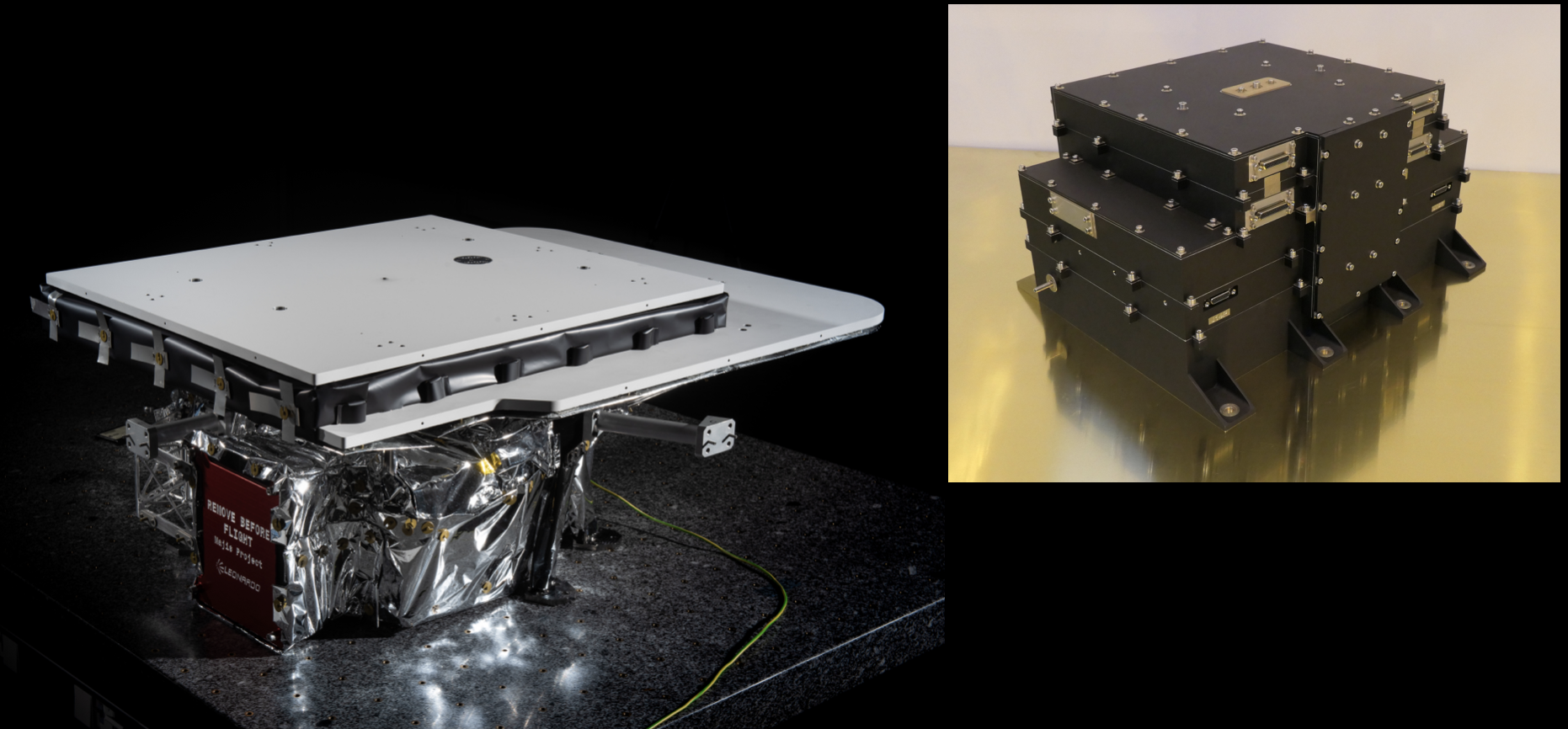
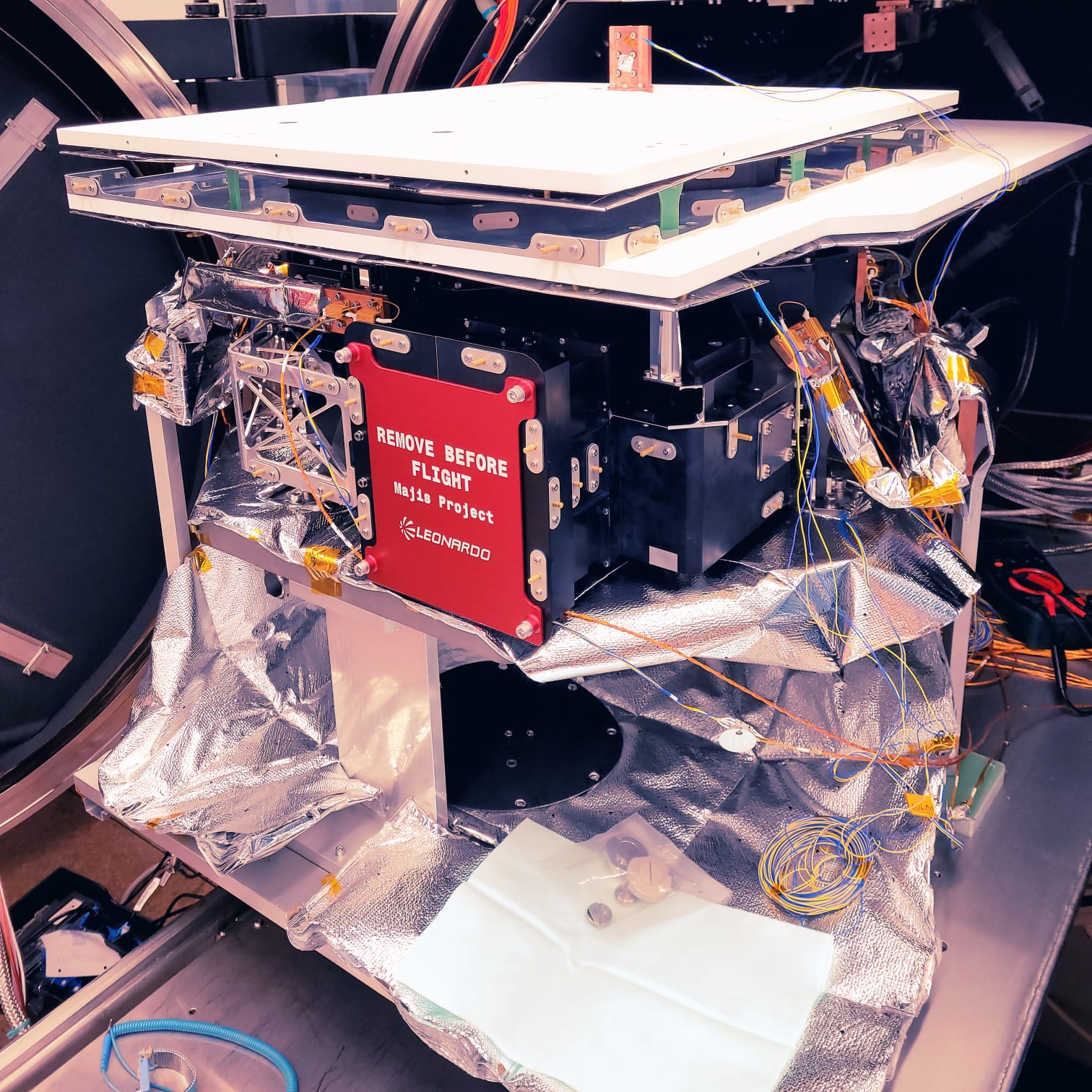
What is MAJIS?
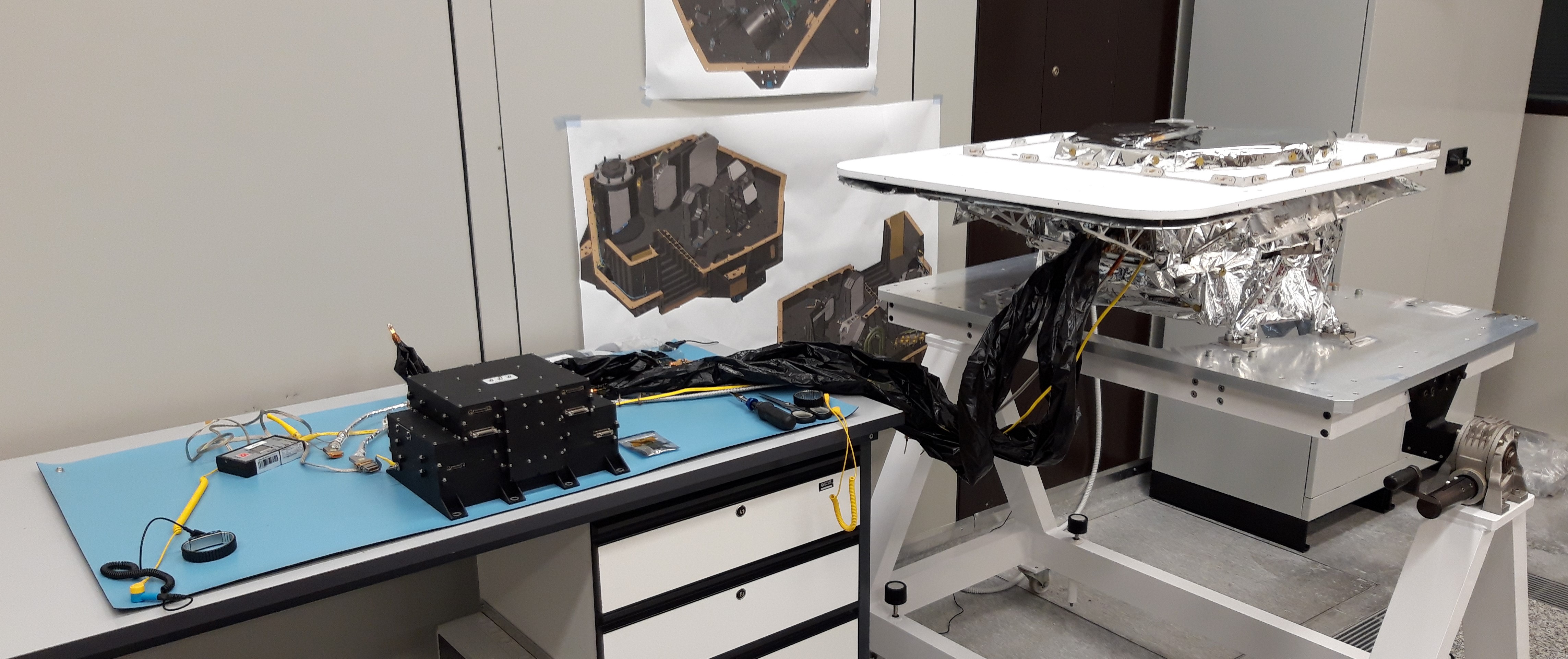
MAJIS (Moons And Jupiter Imaging Spectrometer) is an Italian-French instrument led by the Institut d’Astrophysique Spatiale (IAS) in Paris-Orsay and INAF-IAPS in Rome, and funded in tandem by the French National Centre for Space Studies (CNES) and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The Institute for Space Astrophysics and Planetology (IAPS) of INAF successfully coordinated the original proposal for the instrument (PI Dr. Giuseppe Piccioni) selected by ESA in February 2013. Subsequently, as Co-PI Institute, it then followed the development of the substantial Italian hardware contribution regarding the optical head consisting of a telescope and a spectrometer, built at Leonardo S.p.a. (Campi Bisenzio, Florence), and the evaluation of the expected performances. The flight instrument was assembled, verified, and partly calibrated initially at Leonardo S.p.A., then at IAS-Orsay in Paris. It was finally integrated onboard the JUICE satellite in December 2021.
Some details of the instrument
Among the remote sensing instruments on board JUICE, the MAJIS (Moons and Jupiter Imaging Spectrometer) imaging spectrometer, operating in the visible and near infrared (0.50-5.54 μm), is particularly important for its ability to provide measurements relevant to the entire range of investigations involving the planet Jupiter and its major satellites.
Among these, of utmost importance are the determination and mapping of the surface composition of Jupiter's moons Ganymede, Callisto and Europa, with particular emphasis on compounds other than water ice already known from previous observations or predicted by models, such as hydrated mineral salts, volatiles and organic compounds, and the compositional mapping of the planet's atmosphere, including cloud density and aurora morphology. In this context, the MAJIS project aims to enhance and further develop the skills acquired during the Jovian InfraRed Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) project currently operating around Jupiter on board the NASA Juno mission.

Caratteristiche principali
MAJIS is an imaging spectrometer, also called hyperspectral camera, in the wavelength range between 0.50 and 5.54 µm. The maximum number of spectral channels is 1016 colors for the 400 spatial pixels along the slit. It can reconstruct the two-dimensional image both in scanning mode using its internal mirror, and in push-broom mode utilizing the satellite's motion.
-
Full spectral range: 0.50 e 5.54 µm
-
Number of spectels (bands or colors) in total: 1016
-
Number of pixels along the slit: 400
-
Maximum spatial resolution: 150 m from 1,000 km in distance
-
Full Field Of View: 3.44°
-
Scan capability: internal, push-broom or motion compensation
-
Thermal architecture: total passive by means of radiators
Team

The MAJIS scientific team is composed of 34 co-investigators and 20 associates from different research centers and universities in Italy (22 members), France, Germany, Belgium, Spain, the United Kingdom, and Russia. In addition, many other key figures among technicians and engineers, both Italian and foreign.
The INAF structure most involved, and which coordinates the Italian activity of the instrument, is the IAPS under the responsibility of Dr. Giuseppe Piccioni, with the participation of the astronomical observatory of Catania (OACT, Dr. Maria Elisabetta Palumbo), the CISAS-University of Padua and the Polytechnic of Milan (Prof. Bortolino Saggin).


